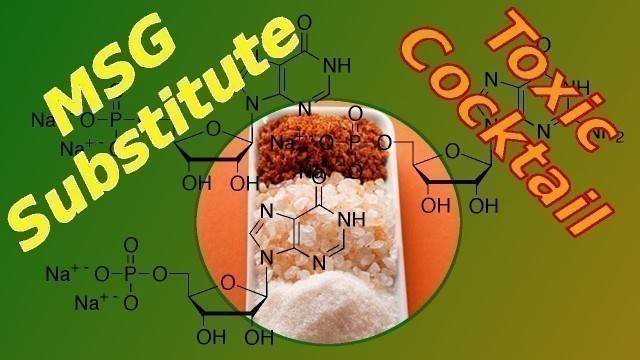

'As people have become aware of the possible side effects and harms of flavor enhancers like MSG, monosodium glutamate, food manufacturers have sought substitutes that can provide flavor enhancement for over-processed lifeless boxed food products. But because of public awareness, the manufacturers also want to be able to avoid specifically listing MSG as one of the ingredients. These new chemicals and substitute flavor enhancers are now causing side effects also, and the general public needs to start recognizing their names on the ingredients labels. Disodium inosinate (E631) is the disodium salt of inosinic acid with the chemical formula C10H11N4Na2O8P. It is used as a food additive and often found in the list of ingredients on the food nutrition label for a great variety of grocery products. Disodium inosinate is used as a flavor enhancer, in synergy with monosodium glutamate MSG (E621) to provide the umami taste. It is often added to foods in conjunction with disodium guanylate; the combination is known as disodium 5\'-ribonucleotides (E635). Flavor Enhancer for Instant Noodles, Pizza, Cheese, Snack Foods, Potato Chips, Crackers, Sauces, Fast Food, Baking Foods, Ice Cream, Canned Foods, Meats, Poultry, Sauces, Soups, Soft Candy, Puddings, Condiments, Snack Food, Fish, Seasonings. As a relatively expensive product, disodium inosinate is usually not used independently of glutamic acid; if disodium inosinate is present in a list of ingredients, but MSG does not appear to be, it is possible that glutamic acid is provided as part of another ingredient or is naturally occurring in another ingredient like tomatoes, Parmesan cheese, or yeast extract. Disodium inosinate, commonly added in fast foods, is essentially a disodium salt of inosinic acid that makes the dish more flavorful. Disodium inosinate is generally produced from meat, including fish and pigs. Though it is normally a non-vegetarian product, it also may be produced from tapioca starch without any animal products involved in the production. The producer can provide information on the origin and it is in some cases labeled as \"vegetarian\" in ingredients lists when produced from plant sources. Generally recognized as safe (GRAS) is an American Food and Drug Administration (FDA) designation that a chemical or substance added to food is considered safe by experts, and so is exempted from the usual Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act (FFDCA) food additive tolerance requirements. Disodium 5′-Ribonucleotides (E635) is considered safe by FDA, meaning it is relatively unregulated. Although it adds a dash of zing to the flavor, people who are sensitive to this flavor enhancer have reported that it can become a toxic cocktail with a whole host of side effects, from mild to severe. Due to its possible side effects, disodium inosinate is not added in foods that are formulated for infants. There is a lot of concern about diet and nutrition for certain demographics, like newborns, children, pregnant women, sensitive to Disodium 5′-Ribonucleotides. Please consult your doctor if you would like to intake Disodium 5′-Ribonucleotides. Better yet, just put the box of processsed non-food back on the shelf and go buy some organic apples and fresh whole veggies. Possible Side Effects Flushed Skin Headache Sweating Burning Sensation Numbness Skin Rash Gastric Discomfort Worsening of Gout Symptoms I am going to be putting together a whole series of similar videos, describing various un-prounounceable chemical compounds that we find on the ingredients labels of many prepared food products on the shelves in the grocery store. Click in the top right corner to link to my video on \"What are Natural Flavors Really Made From?\" - it is a real eye opener that the FDA doesn\'t actually have a definition of the word \"Natural\"! MSDS Safety Data Sheet: http://www.foodchemadditives.com/pdf/en/disodium-5-ribonucleotides-msds.pdf Sources and Additional Information: https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/dsstoxdb/results?search=DTXSID4044242 https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed?LinkName=pccompound_pubmed_mesh&from_uid=135414245 https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/20819 https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Disodium_inosinate https://www.vegsoc.org/info-hub/veggie-need-to-know/e-numbers/?pid=728 http://www.food-info.net/uk/e/e631.htm http://www.chemspider.com/Chemical-Structure.19594.html https://healthhearty.com/side-effects-of-disodium-inosinate https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/scripts/cdrh/cfdocs/cfcfr/CFRSearch.cfm?fr=172.535 Disodium inosinate, Disodium guanylate, Disodium 5\'-Ribonucleotides, MSG, monosodium glutamate substitute, MSG substitute, side effects from flavor enhancers, is msg bad for you, does msg, can msg, disodium inosinate side effects, side effects of junk food, side effects of fast food, bad ingredients in food, what is disodium inosinate,disodium inosinate and guanylate,yeast extract, yeast extract msg,'
Tags: education , trivia , msg , Yeast Extract , side effects of junk food , Side Effects Of fast Food , is msg bad for you , Disodium inosinate , Disodium guanylate , Disodium 5'-Ribonucleotides , monosodium glutamate substitute , MSG substitute , side effects from flavor enhancers , does msg , can msg , disodium inosinate side effects , bad ingredients in food , what is disodium inosinate , disodium inosinate and guanylate , yeast extract msg
See also:

















comments